The art of hand block-printing has been practiced for centuries in India. A process that requires steady movement and careful hand-eye coordination, this traditional technique of fabric printing involves the use of carved wooden blocks that are dipped in dye to recreate gorgeous designs. Block printed fabrics usually showcase a palette of colours that bring these designs to life.
We work with artisans in Jaipur, Rajasthan, which is a key hub of hand block-printing. Certain forms of hand block-printing make use of natural and vegetable dyes, setting this printing technique apart from the rest. Let’s have a look at the technical Block Printing Process.
Step 1: Block Carving
Block carving is the first step in the block printing process and like many other crafts in India, has been in existence since time immemorial. The block-carving artisans make use of tools such as small hammers, chisels and drills to be able to carve elaborate patterns into wooden blocks.
After the carving process, these blocks are dipped in mustard oil and allowed to rest for at least a week. This helps prevent cracking of the blocks upon exposure to dry conditions. The carvers also drill miniature holes into the wooden blocks to allow the wood to breathe. This also extends the life of a wooden block by upto a few decades.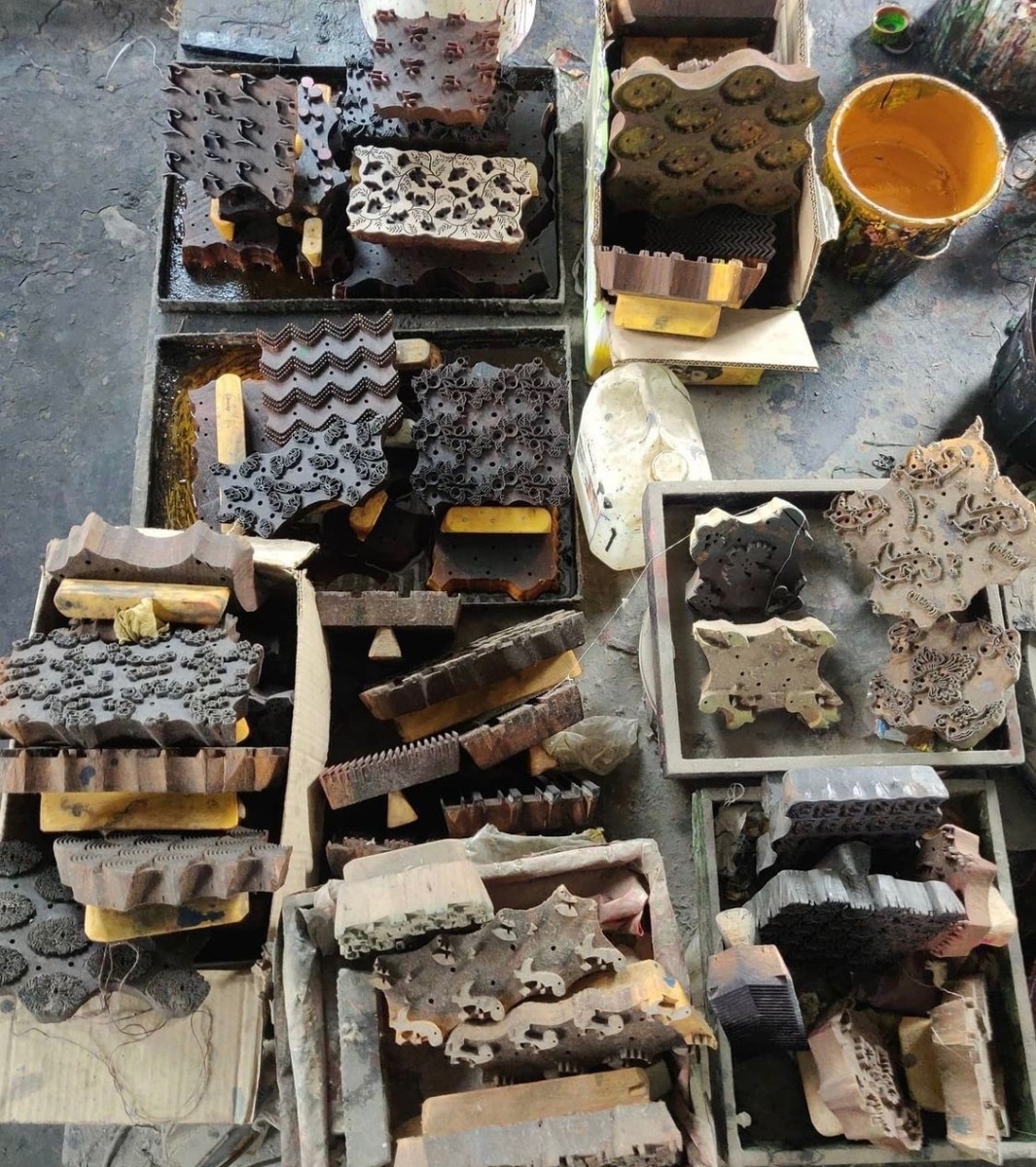
Step 2: Application of Dye
After the carving process, dye is applied to the wooden block surface with the help of a ‘sieve’. The wooden block is gently pressed onto the palette of dye before being applied against the fabric.
Step 3: Treatment of Fabric
The chosen fabric for block printing is first washed to remove all the starch. Fabrics such as saree lengths usually require dyeing. This is done before the printing process begins. For hand block printing, the craftsman will lay the fabric on a printing table, stretching it across the entire length and hold it in place with tiny pins.
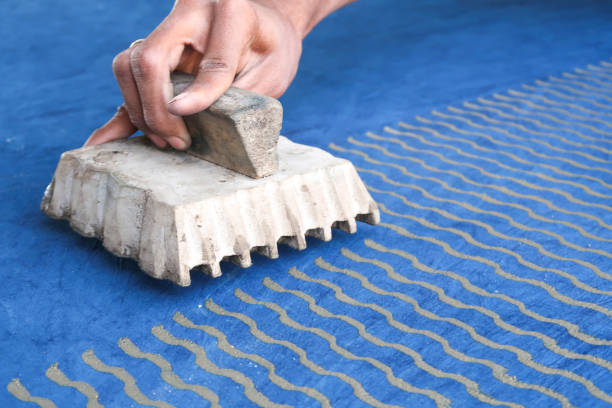
Step 4: Printing
Block printing has a special technique that needs to be followed in order to get the desired results. Printing always begins from left to right. A plank of wood is used to even out the colour on the tray. The craftsman dips the block into a dark outline colour and applies it to the fabric. This is done repeatedly along the length and breadth of the fabric.
Step 5: After Treatment
Once the hand block-printing process is complete, the craftsman scatters some fine saw dust onto the wet dye to prevent smudging of the design. The fabric is then left to dry out in the Sun. Different dyes may be used for block printing on cotton and silk fabrics. Some of the common cotton dyes include indigo sol, pigment dyes and rapid dyes. The traditional colours used for block printing are red, black, brown, mustard and orange.